linuxserver/netbootxyz¶
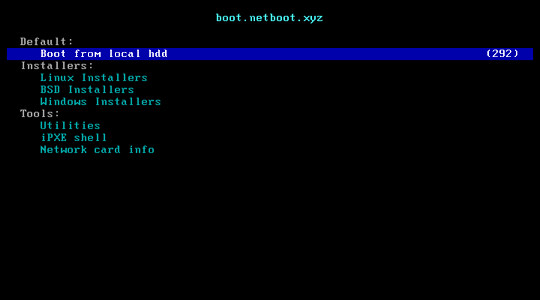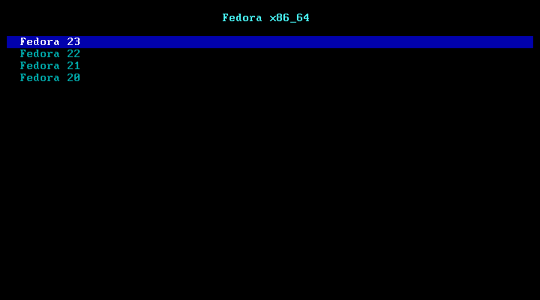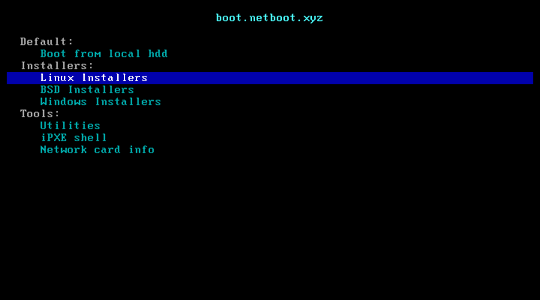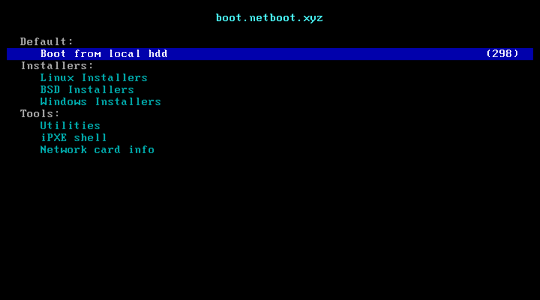
Netbootxyz is a way to PXE boot various operating system installers or utilities from one place within the BIOS without the need of having to go retrieve the media to run the tool. iPXE is used to provide a user friendly menu from within the BIOS that lets you easily choose the operating system you want along with any specific types of versions or bootable flags.
Supported Architectures¶
We utilise the docker manifest for multi-platform awareness. More information is available from docker here and our announcement here.
Simply pulling lscr.io/linuxserver/netbootxyz:latest should retrieve the correct image for your arch, but you can also pull specific arch images via tags.
The architectures supported by this image are:
| Architecture | Available | Tag |
|---|---|---|
| x86-64 | ✅ | amd64-<version tag> |
| arm64 | ✅ | arm64v8-<version tag> |
| armhf | ❌ |
Version Tags¶
This image provides various versions that are available via tags. Please read the descriptions carefully and exercise caution when using unstable or development tags.
| Tag | Available | Description |
|---|---|---|
| latest | ✅ | Web application for full self hosting |
| tftp | ✅ | TFTP server only with NETBOOT.XYZ boot files |
Application Setup¶
To use this image you need an existing DHCP server where you can set this TFTP server as your DHCP boot destination. This image does not contain a DHCP server nor do we aim to support one in the future. This is simply a TFTP server hosting the latest IPXE kernel builds from netboot.xyz. If you are interested in their project and lack the ability to setup a DHCP server to boot this payload they also have USB stick images you can use available on their downloads page.
Router Setup Examples¶
PFSense¶
Services -> DHCP Server
Set both the option for "TFTP Server" and the options under the Advanced "Network Booting" section.n * check enable * Next server- IP used for TFTP Server * Default BIOS file name- netboot.xyz.kpxe * UEFI 32 bit file name- netboot.xyz.efi * UEFI 64 bit file name- netboot.xyz.efi
OPNsense¶
Services -> DHCP Server
Under the Advanced "Network Booting" section. * check enable * Next server- IP of docker host * Default BIOS file name- netboot.xyz.kpxe * UEFI 32 bit file name- netboot.xyz.efi * UEFI 64 bit file name- netboot.xyz.efi
Unifi Security Gateway (with the controller)¶
Networks -> LAN (or the network you want to boot from) -> ADVANCED DHCP OPTIONS * tick Enable network boot * Server- YOURSERVERIP * Filename- netboot.xyz.kpxe Advanced full support * For USG variants force provisioning a json containing the same config used for EdgeOS (shown below) will fully support netboot. * For UDM variants, creating a valid dnsmasq config and placing in /run/dnsmasq.conf.d will load the config, but will not survive reboots or firmware updates source.
EdgeOS/VyOS¶
Connect via SSH
configure
set service dhcp-server use-dnsmasq enable
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-match=set:bios,60,PXEClient:Arch:00000\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-boot=tag:bios,netboot.xyz.kpxe,,SERVERIP\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-match=set:efi32,60,PXEClient:Arch:00002\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-boot=tag:efi32,netboot.xyz.efi,,SERVERIP\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-match=set:efi32-1,60,PXEClient:Arch:00006\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-boot=tag:efi32-1,netboot.xyz.efi,,SERVERIP\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-match=set:efi64,60,PXEClient:Arch:00007\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-boot=tag:efi64,netboot.xyz.efi,,SERVERIP\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-match=set:efi64-1,60,PXEClient:Arch:00008\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-boot=tag:efi64-1,netboot.xyz.efi,,SERVERIP\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-match=set:efi64-2,60,PXEClient:Arch:00009\"
set service dns forwarding options \"dhcp-boot=tag:efi64-2,netboot.xyz.efi,,SERVERIP\"
commit; save
Dnsmasq/DD-WRT/OpenWRT/Tomato/PIHOLE¶
Various locations to set Additional/Custom DNSMASQ options in UI or config files Set the following lines:
dhcp-match=set:bios,60,PXEClient:Arch:00000
dhcp-boot=tag:bios,netboot.xyz.kpxe,,YOURSERVERIP
dhcp-match=set:efi32,60,PXEClient:Arch:00002
dhcp-boot=tag:efi32,netboot.xyz.efi,,YOURSERVERIP
dhcp-match=set:efi32-1,60,PXEClient:Arch:00006
dhcp-boot=tag:efi32-1,netboot.xyz.efi,,YOURSERVERIP
dhcp-match=set:efi64,60,PXEClient:Arch:00007
dhcp-boot=tag:efi64,netboot.xyz.efi,,YOURSERVERIP
dhcp-match=set:efi64-1,60,PXEClient:Arch:00008
dhcp-boot=tag:efi64-1,netboot.xyz.efi,,YOURSERVERIP
dhcp-match=set:efi64-2,60,PXEClient:Arch:00009
dhcp-boot=tag:efi64-2,netboot.xyz.efi,,YOURSERVERIP
Microsoft Server DHCP¶
- Run the DHCP program
- Under Scope/Scope Options
- check option 066 and enter the FQDN or IP of your TFTP boot server
- check option 067 and enter one of the following bootfile names:
- Default BIOS file name- netboot.xyz.kpxe
- UEFI 32 bit file name- netboot.xyz.efi
- UEFI 64 bit file name- netboot.xyz.efi
Anything else from a router standpoint is a crapshoot for supporting Dnsmasq options or proprietary PXE boot options, check Google for support (try your exact router model number with 'pxe boot') or look into setting up your own DHCP server in Linux. This image also contains netboot.xyz.efi which can be used to boot using UEFI network boot. The UEFI boot and menu will have limited functionality if you choose to use it.
Usage¶
To help you get started creating a container from this image you can either use docker-compose or the docker cli.
docker-compose (recommended, click here for more info)¶
---
services:
netbootxyz:
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/netbootxyz:latest
container_name: netbootxyz
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=Etc/UTC
- MENU_VERSION=1.9.9 #optional
- PORT_RANGE=30000:30010 #optional
- SUBFOLDER=/ #optional
- NGINX_PORT=80 #optional
- WEB_APP_PORT=3000 #optional
volumes:
- /path/to/netbootxyz/config:/config
- /path/to/assets:/assets #optional
ports:
- 3000:3000
- 69:69/udp
- 8080:80 #optional
restart: unless-stopped
docker cli (click here for more info)¶
docker run -d \
--name=netbootxyz \
-e PUID=1000 \
-e PGID=1000 \
-e TZ=Etc/UTC \
-e MENU_VERSION=1.9.9 `#optional` \
-e PORT_RANGE=30000:30010 `#optional` \
-e SUBFOLDER=/ `#optional` \
-e NGINX_PORT=80 `#optional` \
-e WEB_APP_PORT=3000 `#optional` \
-p 3000:3000 \
-p 69:69/udp \
-p 8080:80 `#optional` \
-v /path/to/netbootxyz/config:/config \
-v /path/to/assets:/assets `#optional` \
--restart unless-stopped \
lscr.io/linuxserver/netbootxyz:latest
Parameters¶
Containers are configured using parameters passed at runtime (such as those above). These parameters are separated by a colon and indicate <external>:<internal> respectively. For example, -p 8080:80 would expose port 80 from inside the container to be accessible from the host's IP on port 8080 outside the container.
Ports (-p)¶
| Parameter | Function |
|---|---|
3000 | Web configuration interface. |
69/udp | TFTP Port. |
80 | NGINX server for hosting assets. |
Environment Variables (-e)¶
| Env | Function |
|---|---|
PUID=1000 | for UserID - see below for explanation |
PGID=1000 | for GroupID - see below for explanation |
TZ=Etc/UTC | specify a timezone to use, see this list. |
MENU_VERSION=1.9.9 | Specify a specific version of boot files you want to use from NETBOOT.XYZ (unset pulls latest) |
PORT_RANGE=30000:30010 | Specify the port range tftp will use for data transfers (see Wikipedia) |
SUBFOLDER=/ | Specify a subfolder if running this behind a reverse proxy (IE /proxy/) |
NGINX_PORT=80 | Specify a different internal port for the asset server |
WEB_APP_PORT=3000 | Specify a different internal port for the configuration UI |
Volume Mappings (-v)¶
| Volume | Function |
|---|---|
/config | Storage for boot menu files and web application config |
/assets | Storage for NETBOOT.XYZ bootable assets (live CDs and other files) |
Miscellaneous Options¶
| Parameter | Function |
|---|---|
Environment variables from files (Docker secrets)¶
You can set any environment variable from a file by using a special prepend FILE__.
As an example:
Will set the environment variable MYVAR based on the contents of the /run/secrets/mysecretvariable file.
Umask for running applications¶
For all of our images we provide the ability to override the default umask settings for services started within the containers using the optional -e UMASK=022 setting. Keep in mind umask is not chmod it subtracts from permissions based on it's value it does not add. Please read up here before asking for support.
User / Group Identifiers¶
When using volumes (-v flags), permissions issues can arise between the host OS and the container, we avoid this issue by allowing you to specify the user PUID and group PGID.
Ensure any volume directories on the host are owned by the same user you specify and any permissions issues will vanish like magic.
In this instance PUID=1000 and PGID=1000, to find yours use id your_user as below:
Example output:
Docker Mods¶
We publish various Docker Mods to enable additional functionality within the containers. The list of Mods available for this image (if any) as well as universal mods that can be applied to any one of our images can be accessed via the dynamic badges above.
Support Info¶
-
Shell access whilst the container is running:
-
To monitor the logs of the container in realtime:
-
Container version number:
-
Image version number:
Updating Info¶
Most of our images are static, versioned, and require an image update and container recreation to update the app inside. With some exceptions (noted in the relevant readme.md), we do not recommend or support updating apps inside the container. Please consult the Application Setup section above to see if it is recommended for the image.
Below are the instructions for updating containers:
Via Docker Compose¶
-
Update images:
-
All images:
-
Single image:
-
-
Update containers:
-
All containers:
-
Single container:
-
-
You can also remove the old dangling images:
Via Docker Run¶
-
Update the image:
-
Stop the running container:
-
Delete the container:
-
Recreate a new container with the same docker run parameters as instructed above (if mapped correctly to a host folder, your
/configfolder and settings will be preserved) -
You can also remove the old dangling images:
Image Update Notifications - Diun (Docker Image Update Notifier)¶
Tip
We recommend Diun for update notifications. Other tools that automatically update containers unattended are not recommended or supported.
Building locally¶
If you want to make local modifications to these images for development purposes or just to customize the logic:
git clone https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-netbootxyz.git
cd docker-netbootxyz
docker build \
--no-cache \
--pull \
-t lscr.io/linuxserver/netbootxyz:latest .
The ARM variants can be built on x86_64 hardware using multiarch/qemu-user-static
Once registered you can define the dockerfile to use with -f Dockerfile.aarch64.
Versions¶
- 30.06.24: - Rebase to Alpine 3.20.
- 24.02.24: - Add new port settings for the webserver and app.
- 08.12.23: - Rebase to Alpine 3.19.
- 17.11.23: - Rebase to Alpine 3.18.
- 01.07.23: - Deprecate armhf. As announced here
- 05.03.23: - Rebase to Alpine 3.17.
- 12.10.22: - Rebasing to Alpine 3.16, migrate to s6v3.
- 29.04.21: - Rebasing to alpine 3.13, add SUBFOLDER env variable.
- 01.06.20: - Rebasing to alpine 3.12.
- 19.12.19: - Rebasing to alpine 3.11.
- 13.12.19: - Swapping latest tag over to webapp stack for management.
- 10.12.19: - Adding tftp branch to provide tftp only option to latest users.
- 22.10.19: - Initial release.